
SPECT Imaging and TBI
SPECT (Single-photon emission tomography) imaging is emerging as a necessary tool in the evaluation and treatment of patients with TBI (traumatic brain injury) based on…


SPECT (Single-photon emission tomography) imaging is emerging as a necessary tool in the evaluation and treatment of patients with TBI (traumatic brain injury) based on…
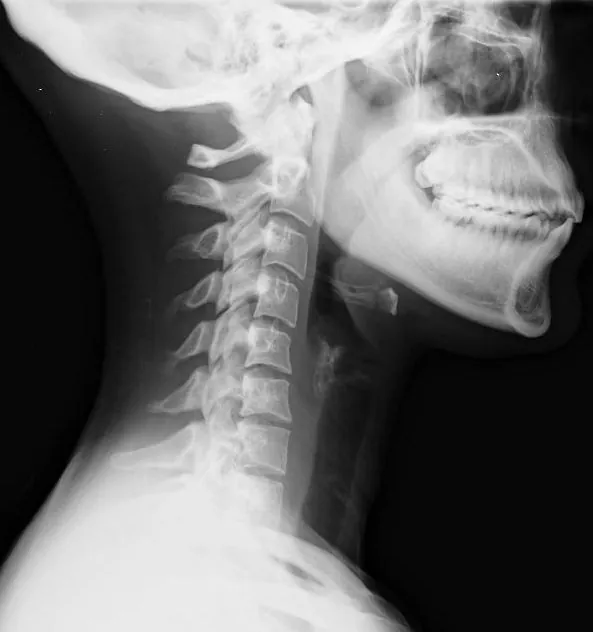
Personal injury victims, especially those who have been injured as a result of a rear-end collision, often suffer from painful injuries as a result of…

In some cases, patients sustaining trauma to the head and neck area will have both closed head injuries and maxillofacial trauma. Of the two, closed…

Craniofacial trauma in children involves any injury to the face, upper jaw bone, or skull. It can include skeletal injury, skin injuries and injuries to…

A medical study was done from 1978-1982 that looked at 196 patients who suffered blunt trauma to the colon, small bowel or mesentery. They were…

Among children, 60 percent of amputations are congenital in nature and 40 percent are acquired due to an injury. Most of these patients require some…

Approximately 300,000 injuries involving doors need treatment at an emergency room each year in the U.S. Most of the victims are children of preschool age…

Water sports are becoming more popular around the world. People are spending more time racing boats, water skiing, scuba diving and skin diving. Injuries because…

Microsurgery is one of the latest types of surgery to develop. It involves doing surgery to blood vessels and nerves underneath a microscope. It is…

Children have a higher likelihood of being injured or killed from trains than adults. They like to play on train tracks and have a lesser…

Fingertip accidents are commonplace amputations at home or on the job. Fingertips can slam in doors, in car doors, while chopping food or when clearing…

Approximately every 115 minutes, someone or something is struck by a train; almost 50 % of all collisions happen at railroad crossings when the automatic…

Traumatic hemipelvectomies are rare traumatic injuries with a forty percent mortality rate. It happens when half of the pelvis from the pubic symphysis to the…

Motor vehicle rollover accidents are accidents in which the motor vehicle ends up on its side or on its back. In other words, there is…

Finger amputations may sound small but they really cause a lot of changes in the way the patient performs certain activities, such as punching the…

Subway accidents can have devastating consequences for those involved. In fact, many people do not survive pedestrian versus subway collisions. While the subway system is…