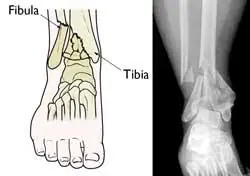
Fractures of the tibia and fibula are not uncommon after a motor vehicle crash. The legs can be crumpled in either the back seat or the front seat from a front end collision. Side collisions can indent the frame of the car inward, resulting in open or closed fractures of the tibia and/or fibula.
Of the two bones in the lower leg, the tibia is the load-bearing bone, while the fibula is simply a stabilizing bone. This makes tibial fractures more problematic than fibular fractures.
Because the skin and subcutaneous tissues are thin over the front and sides of the tibia, many of these fractures are open, meaning the broken ends of the bone protrude through an open wound. Fibular fractures are deeper to the skin so that there are fewer fibular fractures than tibial fractures. Fractures of the fibula are usually in the base of the bone, such as when one turns an ankle. In the tibia, the fracture can involve the tibial plateau or the tibial tubercle, near the knee, the tibial eminence, the proximal, midportion or distal part of the tibia. Some ankle fractures involve portions of the tibia.
Tibial fractures are the most common fractures of the “long bones.” They occur in many types of situations, including motor vehicle accidents. The incidence of open fractures of the long bones of the body are about 11.5 per 100,000 people with about half occurring in the lower leg. Most tibial fractures are in the diaphysis. Isolated fractures of the proximal fibula or the midshaft of the fibula tend to occur quite rarely.
If there is severe disruption of the soft tissue or neurovascular compromise such as damage to the popliteal artery, the leg may need to be removed at the level of the knee or higher. Between the two bones, there is most commonly nonunion or delayed union of the tibia that results in inability to put weight on the foot.
When it comes to “tib/fib” fractures because of a motor vehicle accident, one study looked at factors like age, height, weight, and body mass index on the severity of tibial/fibular fractures. It also looked at factors related to the automobile that prevent or cause these types of fractures. The study looked at 137 people who were in the front seat during a front impact collision. Hip fractures were more common, followed by foot and ankle fractures. Lower leg fractures were present in only 12.1 percent of fractures.
Because women are shorter, they were more likely to have foot and ankle fractures, while men were more likely to sustain hip fractures. Open fractures were much more likely to be associated with the ankle and the tibia. The thing that had the most impact on the degree and placement of fractures was the height of the victim. Female gender was the second thing that indicated a higher than average chance of sustaining a leg or foot fracture.
The treatment of a tibial plus or minus a fibular fracture involves surgical placement of a rod plus cleansing and closing of any open areas.